- Review Article
- Published:
- Hannah E. Davis,
- Lisa McCorkell,
- Julia Moore Vogel &
- Eric J. Topol
Nature Reviews Microbiology (2023)
Abstract
Long COVID is an often debilitating illness that occurs in at least 10% of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infections. More than 200 symptoms have been identified with impacts on multiple organ systems. At least 65 million individuals worldwide are estimated to have long COVID, with cases increasing daily. Biomedical research has made substantial progress in identifying various pathophysiological changes and risk factors and in characterizing the illness; further, similarities with other viral-onset illnesses such as myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome have laid the groundwork for research in the field. In this Review, we explore the current literature and highlight key findings, the overlap with other conditions, the variable onset of symptoms, long COVID in children and the impact of vaccinations. Although these key findings are critical to understanding long COVID, current diagnostic and treatment options are insufficient, and clinical trials must be prioritized that address leading hypotheses. Additionally, to strengthen long COVID research, future studies must account for biases and SARS-CoV-2 testing issues, build on viral-onset research, be inclusive of marginalized populations and meaningfully engage patients throughout the research process.
Conclusions
Long COVID is a multisystemic illness encompassing ME/CFS, dysautonomia, impacts on multiple organ systems, and vascular and clotting abnormalities. It has already debilitated millions of individuals worldwide, and that number is continuing to grow. On the basis of more than 2 years of research on long COVID and decades of research on conditions such as ME/CFS, a significant proportion of individuals with long COVID may have lifelong disabilities if no action is taken. Diagnostic and treatment options are currently insufficient, and many clinical trials are urgently needed to rigorously test treatments that address hypothesized underlying biological mechanisms, including viral persistence, neuroinflammation, excessive blood clotting and autoimmunity.
The impacts of long COVID
The impacts of long COVID on numerous organs with a wide variety of pathology are shown. The presentation of pathologies is often overlapping, which can exacerbate management challenges. MCAS, mast cell activation syndrome; ME/CFS, myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome; POTS, postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome.
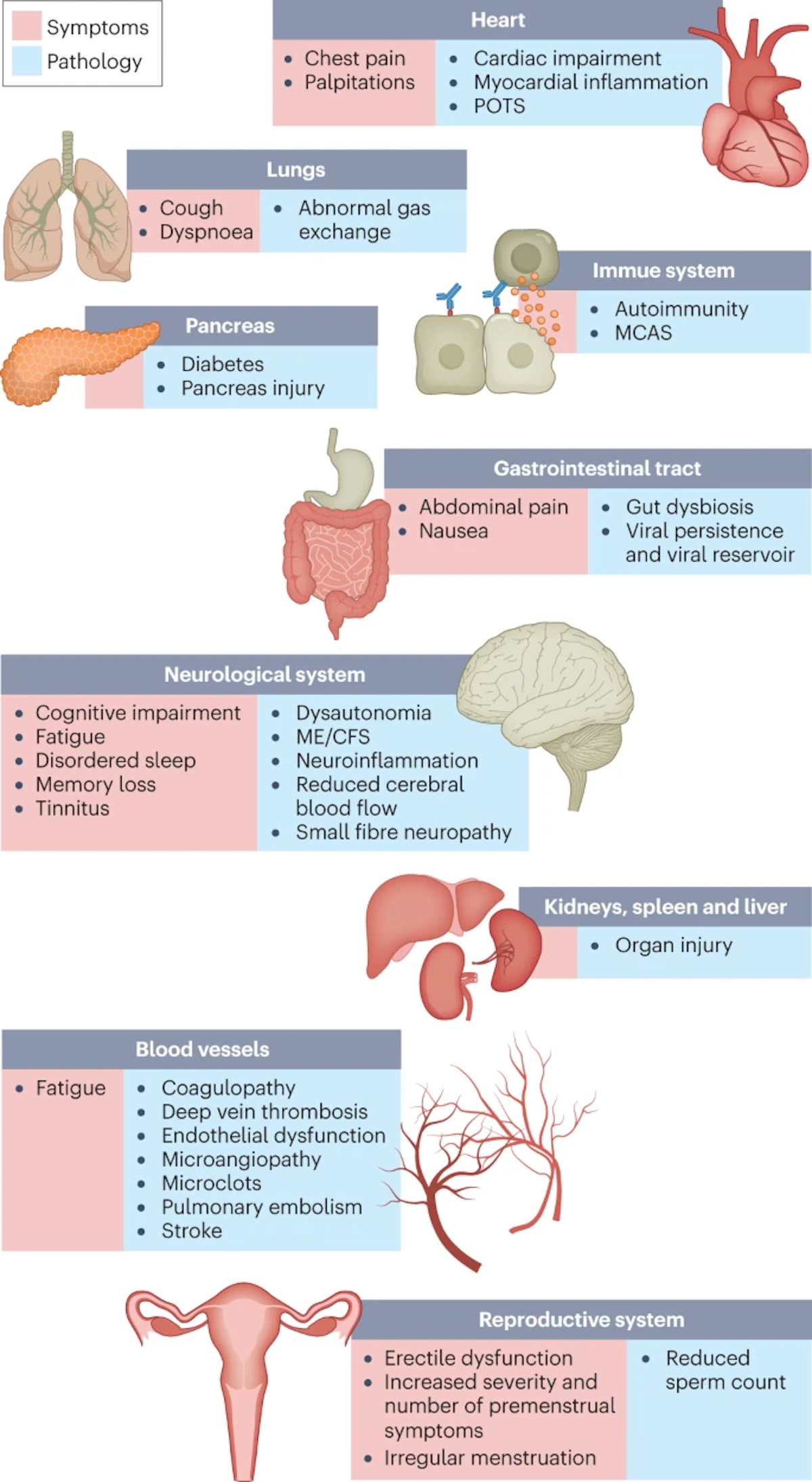
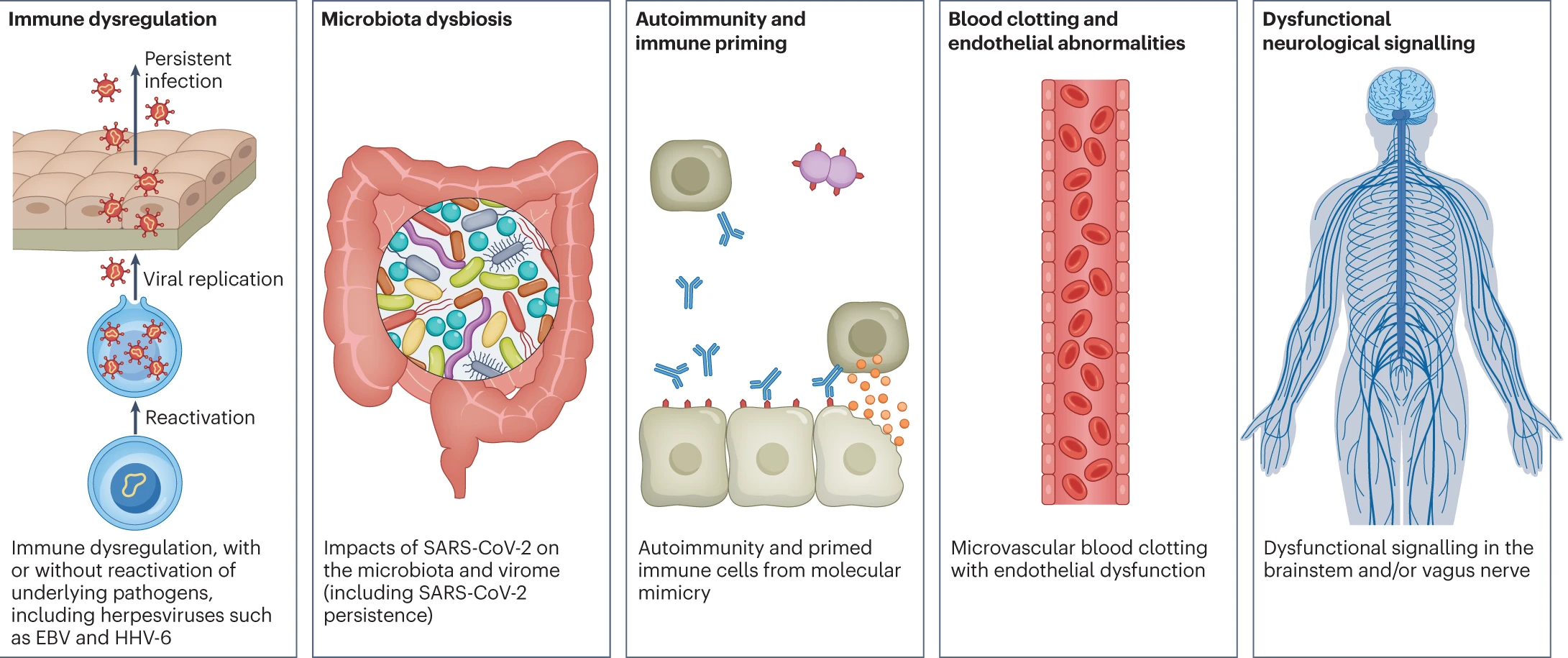
Fig. 3: Hypothesized mechanisms of long COVID pathogenesis.
From: Long COVID: major findings, mechanisms and recommendations Fig. 3 There are several hypothesized mechanisms for long COVID pathogenesis, including immune dysregulation, microbiota disruption, autoimmunity, clotting and endothelial abnormality, and dysfunctional neurological signalling. EBV, Epstein–Barr virus; HHV-6, human herpesvirus 6; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Learn More:
- Long COVID symptoms in SARS-CoV-2-positive children aged 0–14 years and matched controls in Denmark (LongCOVIDKidsDK): a national, cross-sectional study – The Lancet
- Clinical Features and Burden of Postacute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Children and Adolescents – JAMA Network
- Long-COVID in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analyses – Nature
- As the pandemic enters its 4th year, there’s still much to learn about long COVID. Dr. Eric Topol – NPR
