Disinformation can be deadly.
Links for educational purposes:
- The Vaccine Confidence Project
- Ground Truths – Dr. Eric Topol
- A gateway conspiracy? Belief in COVID-19 conspiracy theories prospectively predicts greater conspiracist ideation – PLOS ONE
- Science, misinformation, and the role of education – Science
- Knowledge overconfidence is associated with anti-consensus views on controversial scientific issues – Science Advances
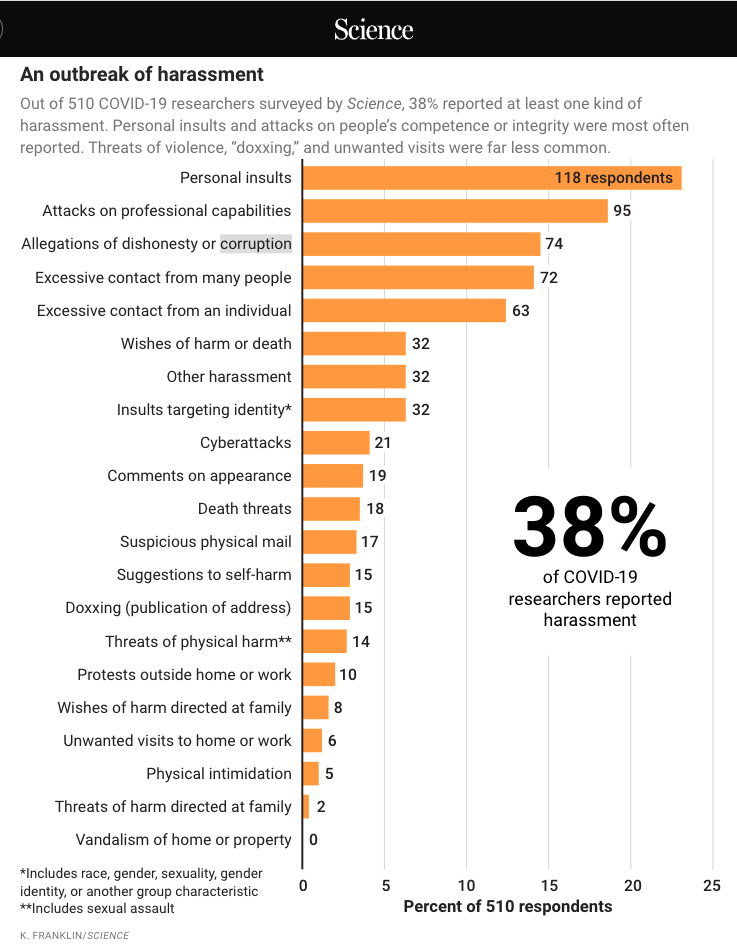
- IN THE LINE OF FIRE. Scientists have been harassed for years. But a Science survey shows the pandemic has made things far worse for some – Science
An epidemic of uncertainty: rumors, conspiracy theories and vaccine hesitancy – Nature Medicine
Abstract
The COVID-19 ‘infodemic’ continues to undermine trust in vaccination efforts aiming to bring an end to the pandemic. However, the challenge of vaccine hesitancy is not only a problem of the information ecosystem and it often has little to do with the vaccines themselves. In this Perspective, we argue that the epidemiological and social crises brought about by COVID-19 have magnified widely held social anxieties and trust issues that, in the unique circumstances of this global pandemic, have exacerbated skepticism toward vaccines. We argue that trust is key to overcoming vaccine hesitancy, especially in a context of widespread social uncertainty brought about by the pandemic, where public sentiment can be volatile. Finally, we draw out some implications of our argument for strategies to build vaccine confidence.
References
-
WHO Director General. Munich Security Conference Speech. http://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/munich-security-conference (2020).
-
Josephson, A. & Lambe, E. Brand communications in time of crisis. Twitter Blog http://blog.twitter.com/en_us/topics/company/2020/Brand-communications-in-time-of-crisis (2020).
-
Loomba, S., de Figueiredo, A., Piatek, S. J., de Graaf, K. & Larson, H. J. Measuring the impact of COVID-19 vaccine misinformation on vaccination intent in the UK and USA. Nat. Hum. Behav. 5, 337–348 (2021).
-
Puri, N., Coomes, E. A., Haghbayan, H. & Gunaratne, K. Social media and vaccine hesitancy: new updates for the era of COVID-19 and globalized infectious diseases. Hum. Vaccines Immunotherapeutics 16, 2586–2593 (2020).
-
Bickert, M. Combatting vaccine misinformation. Facebook Newsroom http://about.fb.com/news/2019/03/combatting-vaccine-misinformation/ (2019).
-
O’Donovan, C. YouTube Just demonetized anti-vax channels. BuzzFeed News http://www.buzzfeednews.com/article/carolineodonovan/youtube-just-demonetized-anti-vax-channels (2019).
-
Center for Countering Digital Hate. The Anti-Vaxx Industry https://www.counterhate.com/anti-vaxx-industry (2020).
-
Bickert, M. How we’re taking action against vaccine misinformation superspreaders. Facebook Newsroom http://about.fb.com/news/2021/08/taking-action-against-vaccine-misinformation-superspreaders/ (2021).
-
Byford, J. Conspiracy Theories: A Critical Introduction (Palgrave Macmillan, 2011).
-
van Prooijen, J.-W. & Douglas, K. M. Conspiracy theories as part of history: the role of societal crisis situations. Mem. Stud. 10, 323–333 (2017).
-
Ahmed, W., Vidal-Alaball, J., Downing, J. & López Seguí, F. COVID-19 and the 5G conspiracy theory: social network analysis of twitter data. J. Med. Internet Res. 22, e19458 (2020).
-
Bruns, A., Harrington, S. & Hurcombe, E. ‘Corona? 5G? or both?’: the dynamics of COVID-19/5G conspiracy theories on Facebook. Media Int. Aust. 177, 12–29 (2020).
-
Waterson, J. & Hern, A. At least 20 UK phone masts vandalised over false 5G coronavirus claims. The Guardian (2020).
-
Frankovic, K. Why won’t Americans get vaccinated? YouGov America https://today.yougov.com/topics/politics/articles-reports/2021/07/15/why-wont-americans-get-vaccinated-poll-data (2021).
-
Larson, H. J. Stuck: How Vaccine Rumors Start – and Why They Don’t Go Away (Oxford Univ. Press, 2020).
-
Kennedy, J. Populist politics and vaccine hesitancy in Western Europe: an analysis of national-level data. Eur. J. Public Health 29, 512–516 (2019).
-
Baumgaertner, B., Carlisle, J. E. & Justwan, F. The influence of political ideology and trust on willingness to vaccinate. PLoS ONE 13, e0191728 (2018).
-
Abalakina-Paap, M., Stephan, W. G., Craig, T. & Gregory, W. L. Beliefs in conspiracies. Political Psychol. 20, 637–647 (1999).
-
Goertzel, T. Belief in conspiracy theories. Political Psychol. 15, 731–742 (1994).
-
Larson, H. J. et al. Measuring trust in vaccination: a systematic review. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 14, 1599–1609 (2018).
-
Ward, J. K. et al. ‘I don’t know if I’m making the right decision’: French mothers and HPV vaccination in a context of controversy. Health Risk Soc. 19, 38–57 (2017).
-
Figueiredo, A., de, Simas, C., Karafillakis, E., Paterson, P. & Larson, H. J. Mapping global trends in vaccine confidence and investigating barriers to vaccine uptake: a large-scale retrospective temporal modelling study. Lancet 396, 898–908 (2020).
-
Razai, M. S., Osama, T., McKechnie, D. G. J. & Majeed, A. Covid-19 vaccine hesitancy among ethnic minority groups. Brit. Med. J. 372, n513 (2021).
-
Wise, J. Pfizer accused of testing new drug without ethical approval. Brit. Med. J. 322, 194 (2001).
-
Jegede, A. S. What led to the Nigerian boycott of the polio vaccination campaign? PLoS Med. 4, e73 (2007).
-
YouGov. YouGov-Cambridge Globalism 2020. https://docs.cdn.yougov.com/msvke1lg9d/Globalism2020%20Guardian%20Conspiracy%20Theories.pdf (2020).
-
Larson, H. J. & Broniatowski, D. A. Volatility of vaccine confidence. Science https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abi6488 (2021).
-
Paterson, P. & Pertwee, E. How will COVID-19 vaccine safety concerns impact vaccine confidence? The BMJ Opinion http://blogs.bmj.com/bmj/2021/04/16/how-will-the-uks-decision-to-offer-an-alternative-to-the-oxford-astrazeneca-covid-19-vaccine-for-under-30s-following-safety-signals-impact-vaccine-confidence/ (2021).
-
YouGov. COVID-19 vaccine willingness tracker https://yougov.co.uk/topics/international/articles-reports/2021/01/12/covid-19-willingness-be-vaccinated (2021).
-
Ofri, D. The emotional epidemiology of H1N1 influenza vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 361, 2594–2595 (2009).
-
Kahneman, D. Thinking, Fast and Slow. (Farrar, Straus and Giroux, 2012).
-
Scrima, F., Miceli, S., Caci, B. & Cardaci, M. The relationship between fear of COVID-19 and intention to get vaccinated. The serial mediation roles of existential anxiety and conspiracy beliefs. Pers. Individ. Dif. 184, 111188 (2022).
-
Gronke, P. The politics and policy of Ebola. Political Sci. Politics 48, 3–18 (2015).
-
Bellato, A. Psychological factors underlying adherence to COVID-19 regulations: a commentary on how to promote compliance through mass media and limit the risk of a second wave. Soc. Sci. Humanities Open 2, 100062 (2020).
-
Goldenberg, A., Garcia, D., Halperin, E. & Gross, J. J. Collective emotions. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 29, 154–160 (2020).
-
Tengbeh, A. F. et al. ‘We are the heroes because we are ready to die for this country’: Participants’ decision-making and grounded ethics in an Ebola vaccine clinical trial. Soc. Sci. Med. 203, 35–42 (2018).
-
Larson, H., Simas, C. & Horton, R. The emotional determinants of health: the lancet–london school of hygiene & tropical medicine commission. Lancet 395, 768–769 (2020).
-
Peretti-Watel, P., Larson, H. J., Ward, J. K., Schulz, W. S. & Verger, P. Vaccine hesitancy: clarifying a theoretical framework for an ambiguous notion. PLoS Curr. https://doi.org/10.1371/currents.outbreaks.6844c80ff9f5b273f34c91f71b7fc289 (2015).
-
Corlett, E. New Zealand gang leaders unite to urge community to get Covid shots. The Guardian https://www.theguardian.com/world/2021/nov/03/new-zealand-vaccines-gang-leaders-unite-covid-shots (2021).
-
de Figueiredo, A., Larson, H. J. & Reicher, S. D. The potential impact of vaccine passports on inclination to accept COVID-19 vaccinations in the United Kingdom: evidence from a large cross-sectional survey and modeling study. EClinicalMedicine 40, 101109 (2021).
-
Roozenbeek, J., S. van der Linden & Nygren, T. Prebunking interventions based on “inoculation” theory can reduce susceptibility to misinformation across cultures. Harvard Kennedy School Misinformation Review 1, 1–23 (2020).
-
Basol, M., Roozenbeek, J. & van der. Linden, S. Good news about bad news: gamified inoculation boosts confidence and cognitive immunity against fake news. J. Cognition 3, 2 (2020).
-
Tariq, K. Finland most resilient to misinformation in classroom milieu. The Academia http://academiamag.com/finland-most-resilient-to-misinformation-in-classroom-milieu/ (2019).

